Using Nitric Oxide as a therapeutic measure can be a successful, rapid, and affordable gamechanger in the fight against the pandemic
In a study involving doctors from the Amrita Hospital, Kochi, and scientists from the School of Biotechnology at Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, a novel intervention for Covid-19 has been explored with the well-known gas Nitric Oxide (NO).
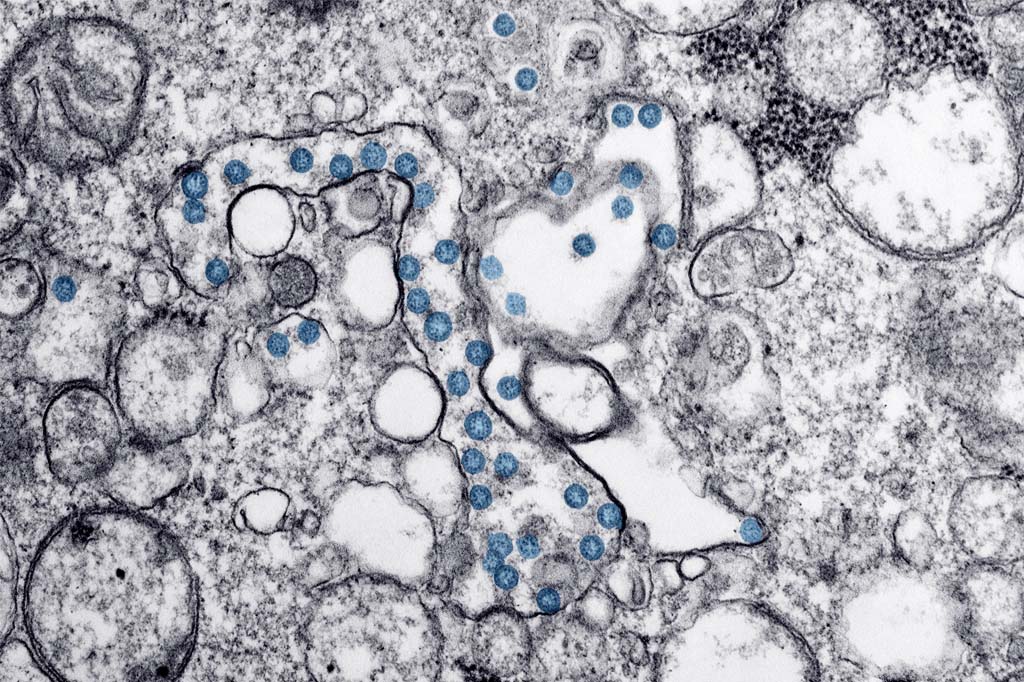
It is colorless, can be produced naturally by the human body, and is important for many aspects of health. Its most vital function is vasodilation, meaning it relaxes the inner muscles of the blood vessels, causing them to widen and increase circulation. This allows blood, nutrients and oxygen to travel to every part of the body effectively and efficiently.
In medical treatment, Nitric Oxide is used worldwide for conditions like Blue Baby Syndrome and for the treatment of heart and lung transplant patients. The study conducted by the Amrita scientists has found that inhaled Nitric Oxide (iNO) is virucidal and kills SARS-COV-2 virus, apart from preventing its effective attachment to human host cells.
In the feasibility trial conducted at Amrita Hospital, Covid-19 patients who received the iNO therapy recovered faster with lesser complications. There was also a zero mortality rate compared to patients who received the standard COVID-19 treatment without iNO.
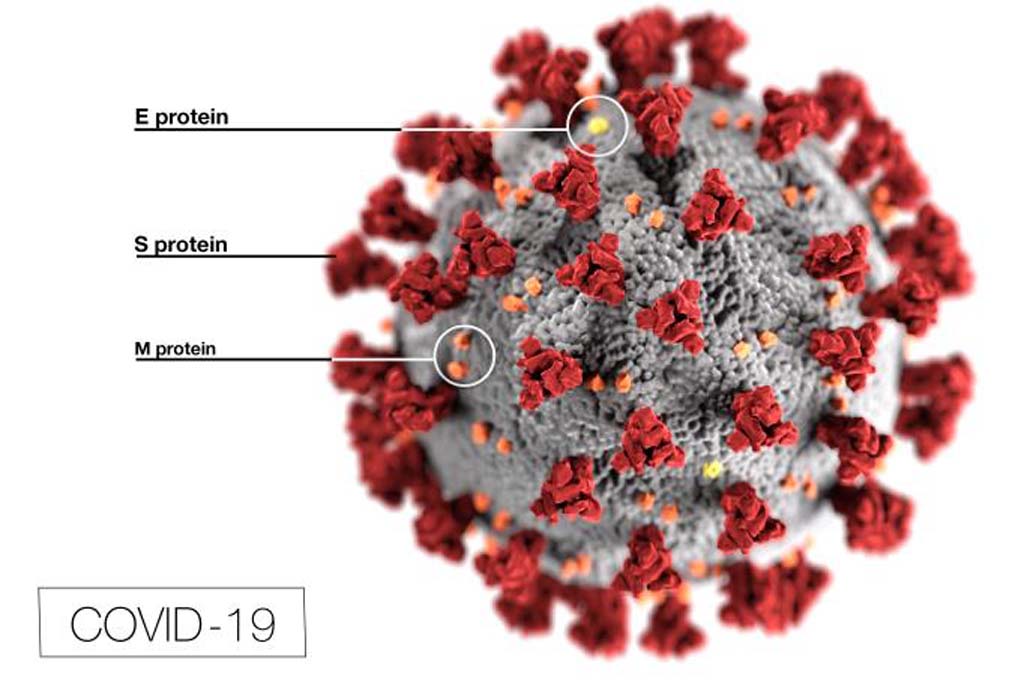
Speaking on the idea behind conducting trials with this novel treatment, Prof. Bipin Nair, Dean, Life Sciences at Amrita School of Biotechnology, said: “Our interest in looking at Nitric Oxide as a treatment option for Covid-19 stemmed from an early study conducted by a Swedish group which had suggested that the gas can prove effective in curbing the SARS-COV-2 virus, as it induces biochemical changes which directly affect the spike protein of the virus. This protein is the main culprit in interacting with our body’s receptors and immune system and creating havoc.”
The team of experts at Amrita Hospital headed by Dr. Aveek Jayant, Dr. Dipu T.S and Dr. Merlin Moni, decided to conduct this trial on a small group of Covid patients admitted at Amrita Hospital. Out of the 25 patients selected for the study, 14 were given iNO along with standard treatment for Covid-19, while 11 patients were in the Control standard treatment group. The patients treated with iNO showed a significant drop in their viral load.
“The study by Amrita Hospital successfully demonstrates the putative role of repurposed inhaled Nitric Oxide in hypoxemic Covid-19 patients. The expert panel associated with the study now calls for an extended validation to take this treatment process to the next level,” said Dr Merlin, Infectious Diseases Division at Amrita Hospital.
“As the global search for an effective remedy against Covid continues, this strategy to use Nitric Oxide as a therapeutic measure has the scope to be a successful, rapid and affordable gamechanger in the fight against the pandemic. It is conceivable that healthcare workers, who are constantly exposed to the coronavirus, could also use this as a prophylactic while treating infected patients,” added Dr Bipin Nair, Dean of Biotechnology at Amrita University.
The study conducted by Amrita scientists has now been published at https://journals.lww.com/imd/Abstract/9000/Clinical_Efficacy_of_Inhaled_Nitric_Oxide_in.99925.aspx
The expert panel associated with it will continue steps to take this treatment process to the next level.
The expert panel of doctors from Amrita Hospital and scientists from the Amrita School of Biotechnology, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, associated with the study included Dr. Aveek Jayant, Head, Dept. of Cardiac Anaesthesiology; Dr. Merlin Mony, and Dr. Dipu TS, Dept. of Infectious Diseases; Dr. Veena Menon, Dept. of Virology, Dr. Geetha Kumar and Dr. Indulekha Pillai and Dr. Bipin Nair, from the Amrita School of Biotechnology; and Dr. Georg Gutjahr, from the varsity’s Centre for Research in Analytics & Technologies for Education.
Dr. Victor Nizet, Professor & Vice Chair for Basic Research at The University of California, San Diego, USA was also closely associated with the study.













